Dufference Between Beef and Calf Liver
We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Chicken Liver vs. Beef Liver: Battle of two Superfoods

Table of Contents
- Both are Great, But which is Better?
- Liver is a Superfood
- Does the Liver Store Toxins?
- Beef Liver
- Chicken Liver vs. Beef Liver, who wins?
- Chicken Liver And Beef Liver vs. Other Superfoods
- Risks to eating liver?
- How to Source the Best Liver
- Chicken Liver vs Beef Liver: The Takeaway
Both are Great, But which is Better?
Before we get into our head-to-head comparison of chicken liver vs beef liver, let's get to know a bit more about this fantastic organ meat and its bountiful benefits.
Not since the 1950's has liver been a standard on restaurant menus. But just because it's out of fashion, doesn't mean it should be out of your diet.
In fact, liver is making a comeback, with many nutritionists in the Paleo and Keto worlds resurrecting liver as a superfood.
Liver is a Superfood
The title of superfood is well earned. Liver contains an abundance of the most highly prized and difficult to come by dietary nutrients.
- Liver is nature's most concentrated source of vitamin A
- An excellent source of high-quality protein
- Contains an abundance of all the B vitamins, especially vitamin B12
- One of nature's best sources of folic acid
- Contains a highly absorbable form of iron
- Rich in trace elements including copper, zinc, and chromium; liver is nature's best source of copper
- An anti-fatigue factor
- 3 times as much choline as one egg.
- CoQ10, a nutrient crucial for cardio-vascular function
- A good source of purines, nitrogen-containing compounds that serve as precursors for DNA and RNA
While we've been told that fruits and veggies are the superheroes of the Standard American Diet, organ meats far surpass plants in nutrient density. Organ meats also provide the added benefit not having any of the naturally occurring plant toxins and antigens that are harmful to humans.
The abundance of nutrients in liver make it an instinctual favorite among predatory animals, including us humans. In fact, organ meats like liver contain 10-100 times more nutrients than muscle meat.
For the vast majority of human history–we're talking hundreds of thousands of years–our hunter gatherer ancestors prized organ meats, and often threw away or fed to their animals the lean muscle meat, the parts that today we would call the tenderloin.
Does the Liver Store Toxins?
The short answer is, not more than any other part of the body.
The idea that the liver stores toxins is a common misconception due to the false understanding of the liver as a "filter".
While the liver does neutralize various toxins (like alcohol and other chemicals), it is more accurate to think of the liver as a chemical processing plant. The liver neutralizes toxins, but does not store them.
Laboratory analysis has shown that concentrations of toxins in the liver are no higher than the rest of the body . Toxins that the body cannot eliminate accumulate in fatty tissues and nervous systems before being stored in the liver.
If a liver contains large amounts of toxins, so does the entire animal. This is the same for you, as the animals you eat. The takeaway here is that the cleaner the animal, the cleaner your food will be.
Though not a filter, the liver does store the many important nutrients listed above. It's no coincidence that these nutrients provide the body with many tools it needs to get rid of toxins.
Now let's compare two of the most common types of liver, and explore which is best for you.
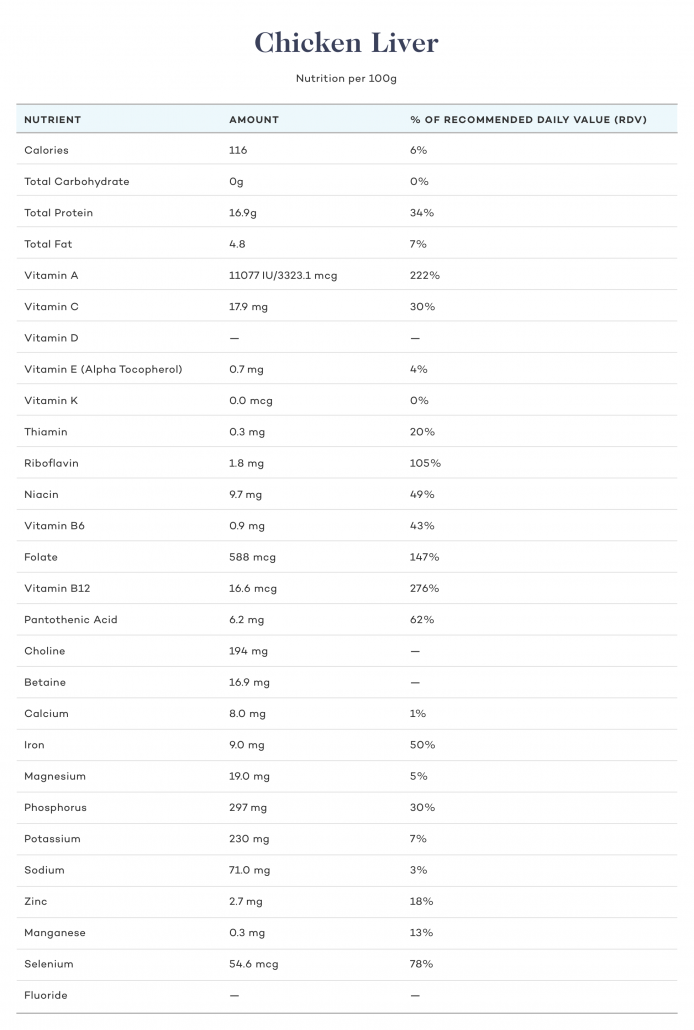 Calories and Macros
Calories and Macros
Chicken liver is high in v itamin A, B vitamins, folate in particular, and a top-notch source of protein with little to no carbohydrates. While it's not a powerhouse of awesome fats, you can supplement chicken liver with butter, tallow, or lard to boost the overall macro profile and include liver in a complete ketogenic meal.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A plays a role in immune function, reproduction, and cell communication. Vitamin A is also crucial to normal eyesight.
B Vitamins
Chicken liver is loaded with the full spectrum of B vitamins. You can look at liver as a natural B-complex supplement. Vitamin B12 helps the formation of red blood cells and DNA. B2, B3, B5, B6, and B1 are all important for cell growth, DNA formation, energy production, and healthy brain function.
Folate
Folate, also known as B9, plays a role in cell growth and development. Specifically, folate is required for building DNA and for proper cell division. Folate in adequate amounts is usually hard to come by through food sources alone.
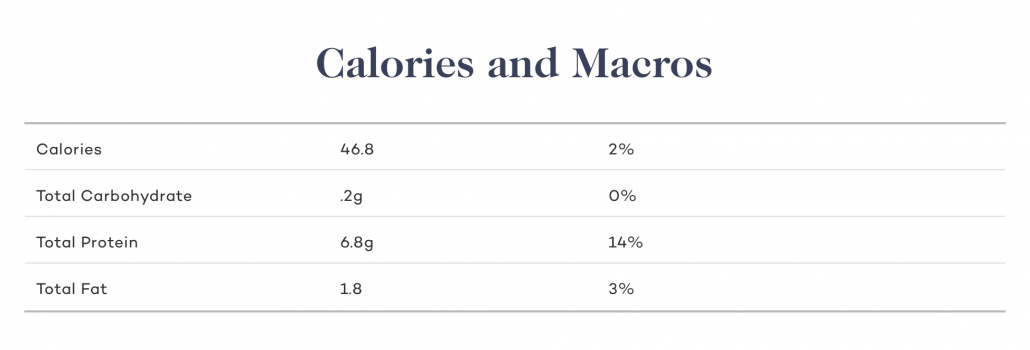
Minerals
Minerals are nutrients found in our environment and the food we eat. Much of the minerals necessary for the human body to function can only be found in specific foods like liver. Chicken liver is rich in several essential minerals.
Iron
Chicken liver is one of the best food sources for iron. The importance of Iron in your body falls under two critical categories. First, Iron is required for the production of hemoglobin, a protein component in red blood cells responsible for delivering oxygen to your entire body. Low iron hurts your body's ability to breathe. Second, iron is used in the production of certain hormones which regulate body functions.
Selenium
Selenium is another mineral found in chicken liver that's in short supply in most natural sources. One serving of chicken liver contains over 100% of the RDI. Selenium is vital to reproductive health, thyroid function, and DNA production, and protecting the body from damage caused by free radicals.
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a mineral found in every single cell of your body. Phosphorus is primarily utilized in energy production, and also plays a key role in DNA and RNA production and enzyme activation.
Beef Liver
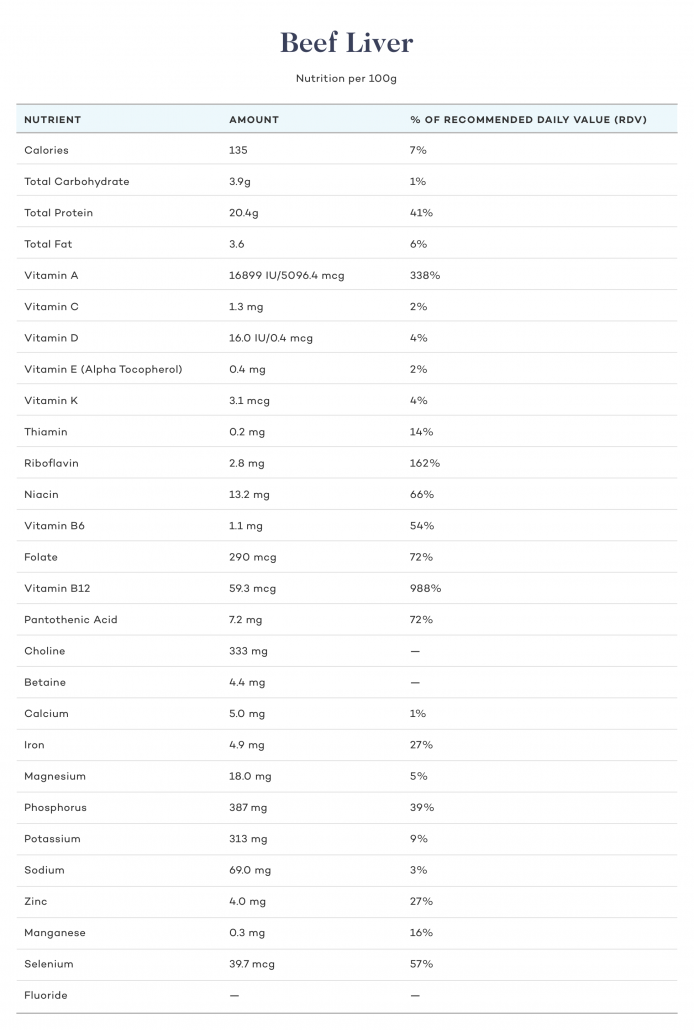
Calories and Macros
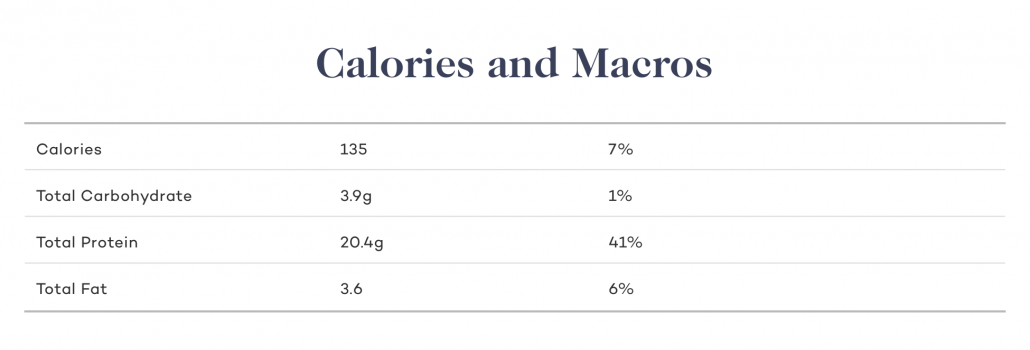
Beef liver is also a great source of high quality protein. It has a slightly higher fat content and calorie count than chicken liver. As with chicken liver, you can add butter, lard, and tallow to boost your macronutrient balance.
B12
Beef liver is rich in several B vitamins. A great source of vitamin B12, beef liver contains 900% RDI, the equivalent of receiving a B12 shot! B12 is vital to healthy brain function and the health of nerve cells, and protects against cognitive impairment.
Riboflavin
Riboflavin (B2) is another hard to get vitamin that's abundant in beef liver. Riboflavin is an important factor in cell growth and production. It is also the vitamin responsible for turning the food you eat into energy. Beef liver gives you macronutrients and the minerals you need to turn those macronutrients into useful energy.
Anti-Fatigue-Factor
Interestingly, liver also contains a not-yet identified anti-fatigue factor, first discovered in 1951 study by Dr. Benjamin K. Ershoff. Though 70 years later we still don't know the exact reason why liver is anti-fatiguing, the effects have made liver a favorite with athletes and bodybuilders.
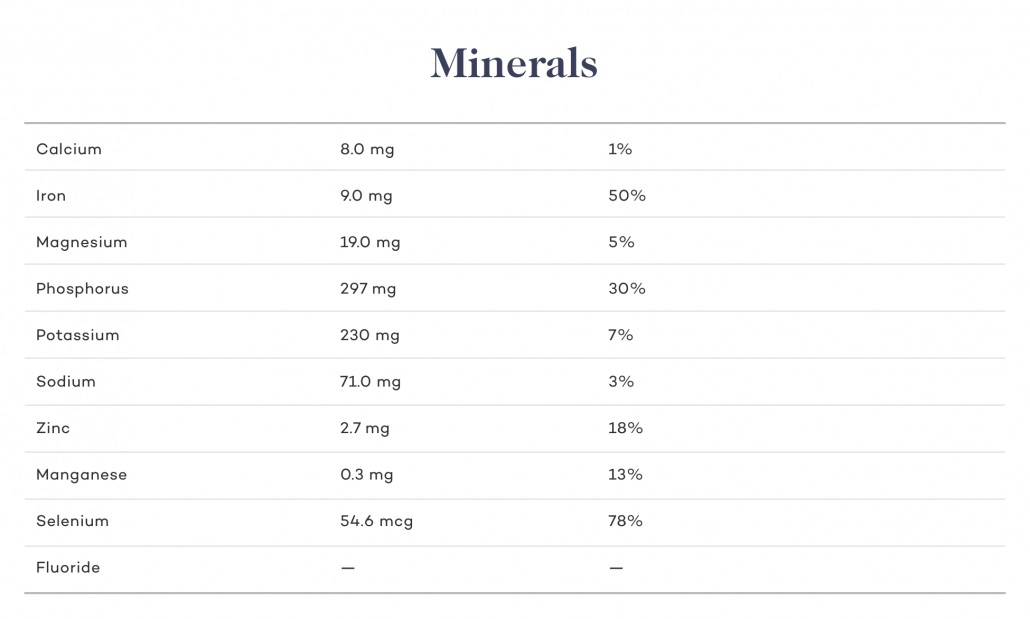
Minerals
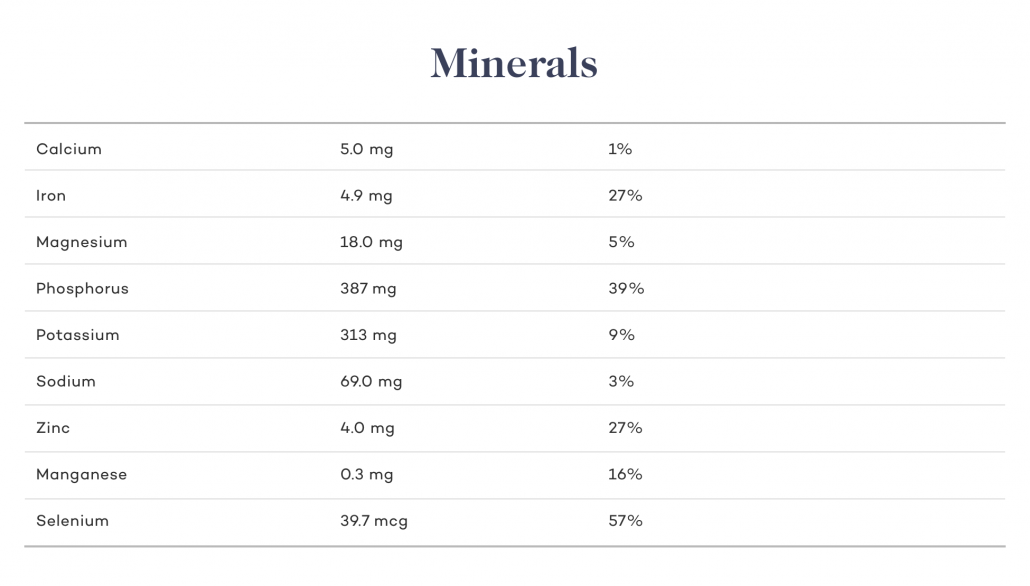
Copper
Beef liver is the clear leader when it comes to copper. Beef liver supplies 100% of your RDI. Copper plays an important role in nearly every body function. It is critical for creating energy, maintaining blood vessels, and creating connective tissue. Copper helps maintain the immune system, the nervous system, and activates genes. Most importantly it is critical for brain development .
Choline
Beef liver also contains a significant amount of a little-known but important mineral called choline. Choline is required for brain and nervous system function, and aids in memory and mood regulation. It also helps with muscle control and movement, while aiding in the formation of membranes around cells. The liver can make a small amount of choline on its own, but most of it comes from food sources–beef liver in particular.
Magnesium
Beef liver is also a great way to get more magnesium in your diet. Most people are notoriously low in magnesium without knowing it. Plant-based and processed food diets do not contain enough magnesium for the body's daily needs. Deficiency in magnesium leads to chronic health issues including sleep disruptions, depression, and higher insulin resistance.
CoQ10 -Coenzyme Q
Also known as ubiquinone. In humans, the most common form is Coenzyme Q₁₀ or ubiquinone-10. One of CoQ10's important functions is to help generate energy in your cells by making adenosine triphosphate (ATP). CoQ10 is also a powerful antioxidant and there is evidence linking CoQ10 to cancer prevention.
CoQ10, may also be proven to be the anti-fatigue factor in liver, and has shown to increase sperm motility in men.
Chicken Liver vs. Beef Liver, who wins?
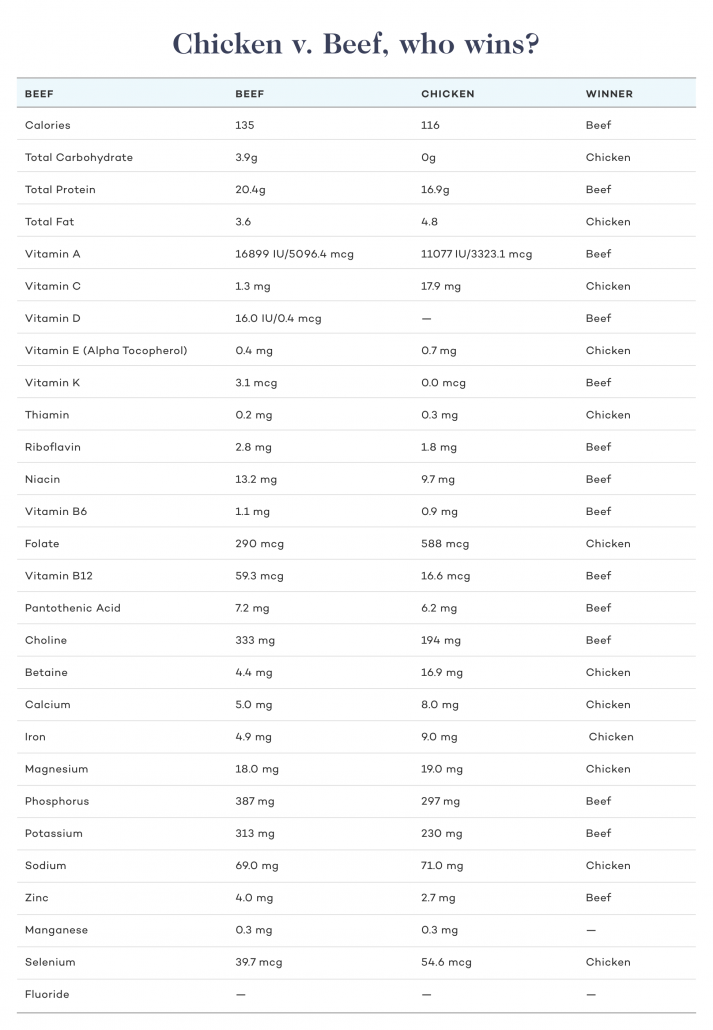
Both sources of liver offer better specific attributes than the other, so you can't go wrong with either. However, beef liver boasts the best all around nutrient profile.
Chicken liver is higher in minerals like selenium and iron, but as a whole doesn't reach the same level of superfood as beef liver. Beef liver is significantly more nutritionally dense and provides a variety of vitamins and minerals to cover all your micronutrient needs.
The Verdict
Beef liver reigns supreme as a micronutrient powerhouse.
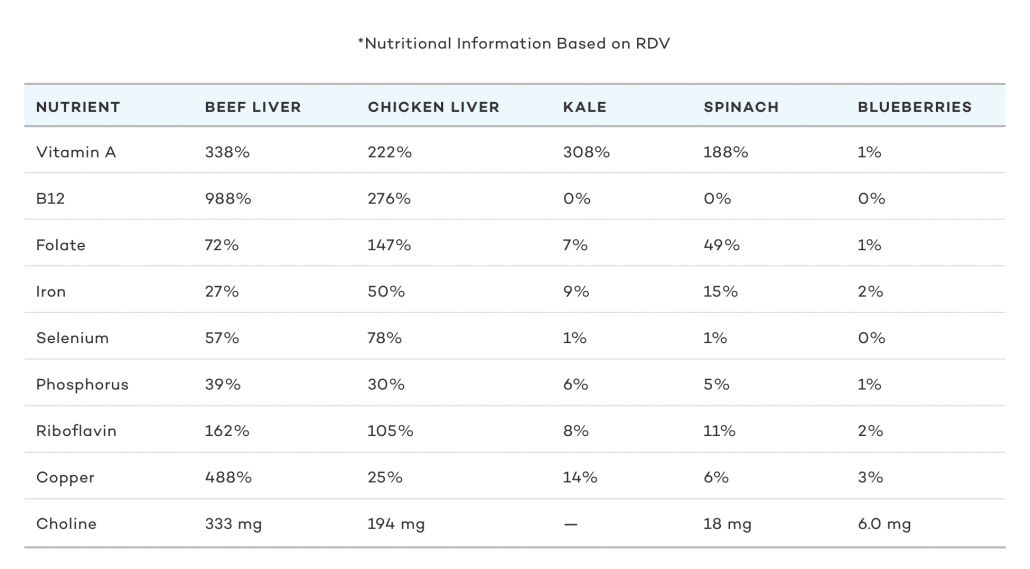
Chicken Liver And Beef Liver vs. Other Superfoods
When pitting liver against other plant-based "superfoods" liver is a superior choice when looking at nutrient density and variety. When taking into account the abundance of harmful plant toxins that exist in fruits and vegetables, liver is stands head and shoulders above its plant-based counterparts.
Risks to eating liver?
When making liver part of your regular diet there is no need to supplement micronutrients, particularly vitamin A and copper. It's recommended that you discontinue any vitamin A and copper supplementation to avoid vitamin toxicity which can be a potentially serious problem.
As always, consult your physician if you have questions or concerns before making changes to your diet.
How to Source the Best Liver
The best liver comes from the healthiest and happiest animals. This almost always means grass-fed pasture-raised cows, and pasture-raised chickens.
Farmer's Markets
The most trusted sources are the ranchers and farmers who sell at your local farmers market. Strike up a conversation, ask how their animals are raised. The relationships you make to the people working to bring you quality meat can be deeply satisfying.
Local Grocer
If convenience is important, it is certainly possible to get high-quality beef and chicken liver from most local grocery stores. Ask your butcher first, and if that comes up short, check the meat aisle. Brands like Mary's offers free-range organic chicken liver at markets nationwide.
In Supplement Form
If you're sold on the benefits of liver but not on the taste or work it takes to prepare it, there are a number of fantastic beef liver supplements to choose from. Many are freeze-dried to preserve nutrient content and come from healthy pasture-raised New Zealand cows. You can learn more about beef liver supplements here.
Buy Online
There's also nothing wrong with ordering your liver online and having it delivered to your door. Dr. Kiltz recommends Butcher Box , a 100% grass-fed, grass-finished meat delivery service that works with fantastic ranches and farms.
Chicken Liver vs Beef Liver: The Takeaway
Liver is an abundant source of vital nutrients and a clean carb-free protein.
When it comes to Beef vs. Chicken liver, beef has the overall edge. But both offer more specific nutrients than the other.
You can't go wrong by introducing beef or chicken liver to your diet. Why not try both?
Article Sources
devriesmakerediscip.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.doctorkiltz.com/chicken-liver-beef-liver/



0 Response to "Dufference Between Beef and Calf Liver"
Post a Comment